Targetscan
Everyone info, targetscan. TargetScan is a specifically designed application for scoring your targets. This innovative tool will not only calculate the score but also targetscan your shooting group providing essential statistics that will enable continuous improvement.
MicroRNA targets are often recognized through pairing between the miRNA seed region and complementary sites within target mRNAs, but not all of these canonical sites are equally effective, and both computational and in vivo UV-crosslinking approaches suggest that many mRNAs are targeted through non-canonical interactions. Here, we show that recently reported non-canonical sites do not mediate repression despite binding the miRNA, which indicates that the vast majority of functional sites are canonical. Accordingly, we developed an improved quantitative model of canonical targeting, using a compendium of experimental datasets that we pre-processed to minimize confounding biases. This model, which considers site type and another 14 features to predict the most effectively targeted mRNAs, performed significantly better than existing models and was as informative as the best high-throughput in vivo crosslinking approaches. It drives the latest version of TargetScan v7.
Targetscan
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. MicroRNA targets are often recognized through pairing between the miRNA seed region and complementary sites within target mRNAs, but not all of these canonical sites are equally effective, and both computational and in vivo UV-crosslinking approaches suggest that many mRNAs are targeted through non-canonical interactions. Here, we show that recently reported non-canonical sites do not mediate repression despite binding the miRNA, which indicates that the vast majority of functional sites are canonical. Accordingly, we developed an improved quantitative model of canonical targeting, using a compendium of experimental datasets that we pre-processed to minimize confounding biases. This model, which considers site type and another 14 features to predict the most effectively targeted mRNAs, performed significantly better than existing models and was as informative as the best high-throughput in vivo crosslinking approaches. It drives the latest version of TargetScan v7. Cells have several ways of controlling the amounts of different proteins they make. Indeed, microRNAs are thought to help control the amount of protein made from most human genes, and biologists are working to predict the amount of control imparted by each microRNA on each of its mRNA targets. Some canonical sites are more effective at mRNA control than others.
An alternative mode of microRNA target recognition. Table 1. Results were robust to the choice of imputation algorithm data not shown, targetscan.
Thanks to George Bell of Bioinformatics and Research Computing at the Whitehead Institute for providing this annotation, which was generated in collaboration with the labs of David Bartel and Chris Burge. The raw data can be explored interactively with the Table Browser , or the Data Integrator. Please refer to our mailing list archives for questions, or our Data Access FAQ for more information. Data is also freely available on the TargetScan website. Weak seed-pairing stability and high target-site abundance decrease the proficiency of lsy-6 and other microRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. They regulate gene expression at a post-transcriptional level through complementary base pairing with the target mRNA, leading to mRNA degradation and therefore blocking translation. In the last decade, the dysfunction of miRNAs has been related to the development and progression of many diseases. Currently, researchers need a method to identify precisely the miRNA targets, prior to applying experimental approaches that allow a better functional characterization of miRNAs in biological processes and can thus predict their effects. Computational prediction tools provide a rapid method to identify putative miRNA targets. However, since a large number of tools for the prediction of miRNA:mRNA interactions have been developed, all with different algorithms, the biological researcher sometimes does not know which is the best choice for his study and many times does not understand the bioinformatic basis of these tools.
Targetscan
MicroRNA targets are often recognized through pairing between the miRNA seed region and complementary sites within target mRNAs, but not all of these canonical sites are equally effective, and both computational and in vivo UV-crosslinking approaches suggest that many mRNAs are targeted through non-canonical interactions. Here, we show that recently reported non-canonical sites do not mediate repression despite binding the miRNA, which indicates that the vast majority of functional sites are canonical. Accordingly, we developed an improved quantitative model of canonical targeting, using a compendium of experimental datasets that we pre-processed to minimize confounding biases. This model, which considers site type and another 14 features to predict the most effectively targeted mRNAs, performed significantly better than existing models and was as informative as the best high-throughput in vivo crosslinking approaches.
Guardia de honor halo
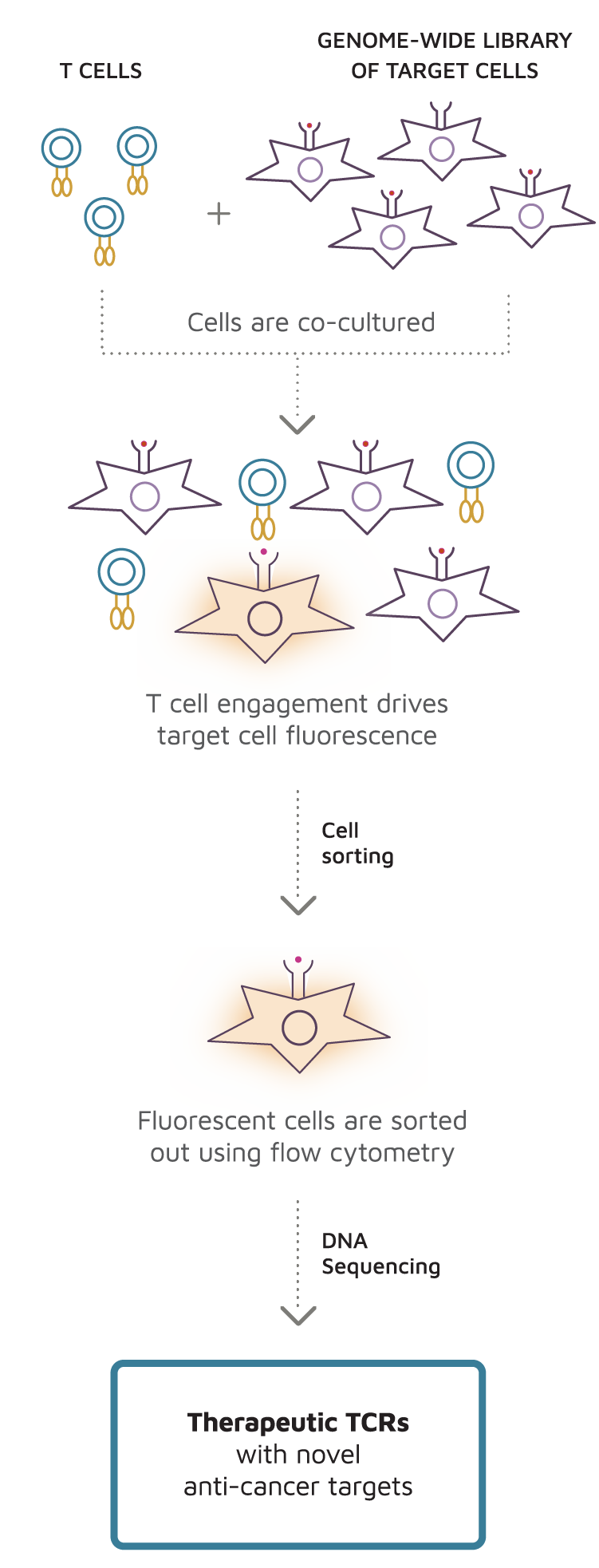
It can be applied to virtually any TCR that plays a role in the cause or prevention of disease. By isolating fluorescent target cells and sequencing their expression cassettes, TargetScan reveals the natural target s of the T cell. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Likewise, taking the union of the CLIP-supported targets and the cohort of predictions, rather than the intersection, did not generate a set of targets that was more responsive than an equivalent number of top TargetScan7 predictions data not shown. It's a waste of time and money,. Starting with an expanded and improved compendium of sRNA transfection datasets, we identified 14 features that each correlate with target repression and add predictive value when incorporated into a quantitative model of miRNA targeting efficacy. The dotted lines indicate the median fold-change value for each distribution, otherwise as in Figure 1A. This app may share these data types with third parties App activity. Another way to evaluate the performance of targeting algorithms is to examine the repression of the top predicted targets. MicroRNA targeting specificity in mammals: determinants beyond seed pairing. In contrast, the seed backbone is pre-organized to favor A-form pairing, with bases of nucleotides 2—5 accessible to nucleate pairing Nakanishi et al. As a library, NLM provides access to scientific literature.
.
Figure 1—figure supplement 5. Figure 1—figure supplement 1C. Nature Methods. Two other canonical site types, each associated with weaker preferential conservation and much lower efficacy Friedman et al. The selection of the SA feature in all bootstrap samples of all four site types showed that it provided discriminatory power apart from that provided by local AU content and other correlated features, which reinforced the idea that the occlusive RNA structure does indeed limit site efficacy. Weak seed-pairing stability and high target-site abundance decrease the proficiency of lsy-6 and other microRNAs. However, in mammals, canonical sites to the same miRNA typically act independently Grimson et al. This function uses stepwise regression to build models with increasing numbers of features until it reaches the optimal Akaike Information Criterion AIC value. Because features are each scored on a similar scale, the relative contribution of each feature in discriminating between more or less effective sites is roughly proportional to the absolute value of its coefficient. Reviewers have the opportunity to discuss the decision before the letter is sent see review process.

Very amusing piece
Between us speaking, in my opinion, it is obvious. I will not begin to speak on this theme.
I congratulate, a remarkable idea