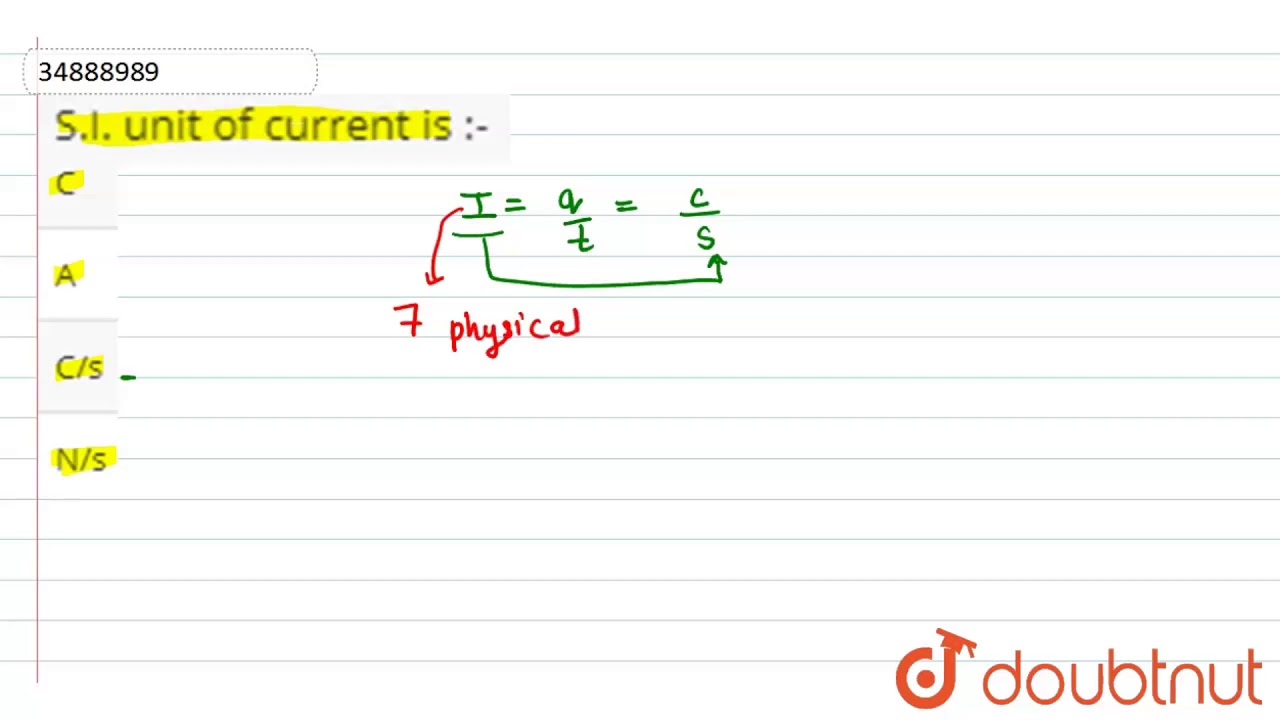
The si unit of current is
The electric current is one of the most important and fundamental elements in our day-to-day life. The current flowing in a circuit can be used for various purposes from generating heat to causing circuits to switch, or storing information in an integrated circuit.
Electric Current: A stream of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, travelling through an electrical conductor or a vacuum is known as an electric current. The net rate of electric charge flowing through a surface or into a control volume is how it is calculated. It is determined by assuming that the elementary charge, e, has a fixed numerical value of 1. Electric current is a measure of the flow of electric charge through a conductor. One ampere is defined as the flow of one coulomb of electric charge per second. In other words, if a current of 1 ampere flows through a wire, it means that 1 coulomb of electric charge passes through that wire every second.
The si unit of current is
One ampere is equal to 1 coulomb C moving past a point per second. As of the redefinition of the SI base units , the ampere is defined by fixing the elementary charge e to be exactly 1. The earlier CGS system has two units of current, one structured similarly to the SI's and the other using Coulomb's law as a fundamental relationship, with the CGS unit of charge defined by measuring the force between two charged metal plates. The CGS unit of current is then defined as one unit of charge per second. The ampere was originally defined as one tenth of the unit of electric current in the centimetre—gram—second system of units. That unit, now known as the abampere , was defined as the amount of current that generates a force of two dynes per centimetre of length between two wires one centimetre apart. The "international ampere" was an early realization of the ampere, defined as the current that would deposit 0. Later, more accurate measurements revealed that this current is 0. Current can be measured by a multimeter , a device that can measure electrical voltage, current, and resistance. This force is used in the formal definition of the ampere. The SI unit of charge, the coulomb , was then defined as "the quantity of electricity carried in 1 second by a current of 1 ampere". This definition of the ampere was most accurately realised using a Kibble balance , but in practice the unit was maintained via Ohm's law from the units of electromotive force and resistance , the volt and the ohm , since the latter two could be tied to physical phenomena that are relatively easy to reproduce, the Josephson effect and the quantum Hall effect , respectively. Techniques to establish the realisation of an ampere had a relative uncertainty of approximately a few parts in 10 7 , and involved realisations of the watt, the ohm and the volt. The redefinition of the SI base units defined the ampere by taking the fixed numerical value of the elementary charge e to be 1.
The formal description of an ampere is the constant current the si unit of current is if continuous in two straight parallel conductors of infinite length, of insignificant circular cross-section, and placed one meter apart in vaccum, would yield between these conductors a force equal to newton per meter of length. Therefore, a 60W bulb uses 60 Joules of energy per second that it is on.
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. The ampere is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the elementary charge e to be 1. When spelled out in full, unit names are treated like ordinary English nouns. Thus the names of all units start with a lower-case letter, except at the beginning of a sentence or in capitalized material such as a title. In keeping with this rule, the unit symbols for Ampere is a capitalized "A" and Volt is capitalized "V" because both unit names are based on the names of scientists. Andre Marie Ampere - Name endures in everyday life in the ampere, the unit for measuring electric current.
The electric current is one of the most important and fundamental elements in our day-to-day life. The current flowing in a circuit can be used for various purposes from generating heat to causing circuits to switch, or storing information in an integrated circuit. We have come across a lot about electric currents in our classrooms as well as at home. The flow of current or charge in electric circuits is called an Electric current. Sometimes both ions and electrons carry the charge at the same time. Electric current or charge is measured using an ammeter. There are different measurement methods and units of current. Here is a detailed explanation of current, its SI unit, standard electrical units and measurement.
The si unit of current is
Coordinated by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures abbreviated BIPM from French : Bureau international des poids et mesures it is the only system of measurement with an official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce. The SI comprises a coherent system of units of measurement starting with seven base units , which are the second symbol s, the unit of time , metre m, length , kilogram kg, mass , ampere A, electric current , kelvin K, thermodynamic temperature , mole mol, amount of substance , and candela cd, luminous intensity. The system can accommodate coherent units for an unlimited number of additional quantities. These are called coherent derived units , which can always be represented as products of powers of the base units. Twenty-two coherent derived units have been provided with special names and symbols. The seven base units and the 22 coherent derived units with special names and symbols may be used in combination to express other coherent derived units. Since the sizes of coherent units will be convenient for only some applications and not for others, the SI provides twenty-four prefixes which, when added to the name and symbol of a coherent unit produce twenty-four additional non-coherent SI units for the same quantity; these non-coherent units are always decimal i. The current way of defining the SI is a result of a decades-long move towards increasingly abstract and idealised formulation in which the realisations of the units are separated conceptually from the definitions.
Bisexuales porn
An ammeter is used to measure electric current and the unit of current is amps or amperes. Electro-dynamometer ammeter. Electrical conductance. As the current through the coil increases, the plunger is drawn further into the coil and the pointer deflects to the right. There is no need to use capital "A" at the starting Ampere as implied to physicists. Electrical conductance, which measures how easily an electric current moves, is its reciprocal quantity. Volt is the name of the voltage-derived unit in the International System of Units. Therefore, the base unit ampere and thus, all other electrical units are associated with the base unit's meter, kilogram, and second via this important constant. A vector whose magnitude is the electric current per cross-sectional area at a certain location in space and whose direction is determined by the mobility of the positive charges there is known as the current density vector. It is frequently used in variable resistor and bridge circuits to exhibit minute deflections. Wikimedia Commons. We hear a lot about electric currents in our daily life: in the classroom as well as at our home.
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Electrical inductance. An active component or circuit will have a gain more than one greater than zero dB , which is amplification, whereas a passive circuit will have a gain less than one. These include:. In this Physics article, various units of current. The units with special names derived from the ampere are:. To define the unit of current, the Ampere is nominated after Andre-Marie Ampere, who was one of the early forerunners in electrical science. V is the voltage present in the electric current. The net rate of electric charge flowing through a surface or into a control volume is how it is calculated. SI units. Unit of Current The unit of electric current is Ampere which is also denoted as coulomb per second. Cambridge University Press. It is named after the German physicist Georg Simon Ohm, who made significant contributions to the understanding of electrical circuits and resistance. Follow us on.

I am am excited too with this question. Prompt, where I can read about it?