Trace mucosal thickening
Federal government websites often end in.
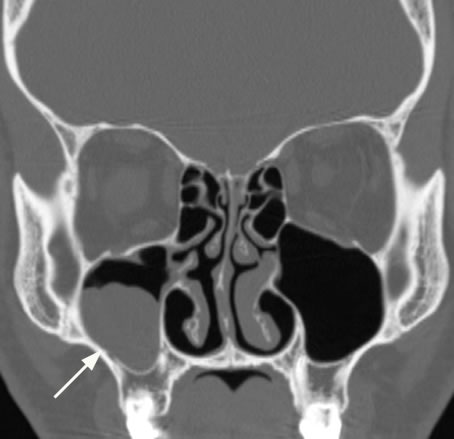
Thickening of mucosa within the paranasal sinuses is frequently detected on diagnostic imaging of the head, even in patients with no apparent rhinologic disease. Previous studies have suggested that mucosal thickening is poorly correlated with sinonasal inflammation, in patients without chronic rhinosinusitis CRS 5 - 8. However, as the paranasal sinuses are only endoscopically accessible in the post-surgical setting, these studies have been unable to correlate imaging with direct endoscopic assessment of the sinuses and have relied upon patient reported symptoms to assess inflammation. In this context, patients who have received surgery for paranasal sinus or skull base tumors provide a convenient population, without CRS, in whom inflammation can be verified endoscopically. This study aimed to determine the diagnostic performance of sinus MRI mucosal thickening, in patients without CRS, using validated endoscopic examination and patient reported symptoms. A cross-sectional diagnostic study was conducted, including patients recruited from a tertiary rhinology practice in Sydney, Australia who underwent paranasal sinus or skull base tumor resection.
Trace mucosal thickening
Sinusitis is inflammation of the lining mucosa of the sinuses. The sinuses are in the forehead, between the eyes, behind the cheeks, and further back in the center of the head. Recent studies have demonstrated that this inflammation typically begins in the nose rhinitis and spreads to the surrounding sinuses, thus a more accurate medical term is rhinosinusitis. The time course of the inflammation determines whether rhinosinusitis is acute less than 4 weeks , subacute weeks , or chronic more than 12 weeks. Recurrent acute sinusitis is frequent bouts of sinus infections that resolve with medications but recur soon after finishing medications. How common is sinusitis? What causes chronic sinusitis? How is sinusitis diagnosed? Who treats sinusitis? What types of sinusitis are there? How are patients treated for sinusitis?
All authors have reached an agreement in terms of the final manuscript. They employ both medical and surgical interventions to provide relief from these conditions and improve patients' quality of life. J Int Acad Periodontol.
One hundred twenty-eight patients were examined prospectively to determine the significance of mucosal thickening seen in the paranasal sinuses during routine MR imaging of the brain. Patients were categorized further on the basis of the maximal mucosal thickening seen by MR in any paranasal sinus. A modified t test was used to compare the prevalence of various degrees of mucosal thickening between symptomatic and asymptomatic groups. Statistically significant differences between the groups were seen only in those patients with normal sinuses and in those with 4 mm or more of mucosal thickening. We conclude that mucosal thickening of up to 3 mm is common and lacks clinical significance in asymptomatic patients. This minimal mucosal thickening in the ethmoidal sinuses is thought to be a normal variant, possibly a function of the physiologic nasal cycle.
Advances in diagnostic imaging techniques e. Diagnostic imaging is generally used in cases of recurrent or complicated sinus disease. Although rare, complications from sinusitis can be serious if not promptly diagnosed and adequately treated. Plain radiography has a limited role in the management of sinusitis. Possible findings in acute sinusitis include mucosal thickening, air-fluid levels, and complete opacification of the involved sinus. Although mucosal thickening is seen in more than 90 percent of sinusitis cases, it is very nonspecific. Because clinical judgment is sufficient to diagnose sinusitis in a majority of cases, and empiric treatments are inexpensive and safe, only a small percentage of patients who develop recurrent or complicated sinusitis are candidates for imaging studies.
Trace mucosal thickening
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Abnormalities can be classified as: non-neoplastic, neoplastic benign, and neoplastic malignant. We found the following disease frequencies: focal mucoperiosteal thickening There was no significant difference between male and female, and Groups A, B, or C when relating the frequencies of abnormalities found. There was no significant difference between male and female and the age group for the side of the altered maxillary sinus. Mucoperiosteal thickening; acute, chronic, and odontogenic sinusitis; polypoid lesions and neoplasms have high prevalence in maxillary sinuses. Thus, facial CT exam was effective for the evaluation of diseases in maxillary sinuses. The facial region is formed in general, by oral cavity, jaw bones, nose and paranasal sinuses. Due to the wide anatomic proximity between the facial structures, diseases in one component can easily affect others.
Someone down to earth crossword clue
Analysis of variance ANOVA was applied to compare the risk factors for furcation lesions and vertical infrabony pockets. Class 0 1. This predisposes them to have significant inflammation in the sinus lining triggered by certain environmental factors. In this context, patients who have received surgery for paranasal sinus or skull base tumors provide a convenient population, without CRS, in whom inflammation can be verified endoscopically. There are a few things that may increase your chance of bleeding. Non-sinus headaches can also occur in similar locations, but they usually will not be accompanied by nasal symptoms. Your doctor will show you how this works. These patients often have diffuse inflammation on both sides of their nose, but this type of sinusitis is not associated with asthma and allergies as often as sinusitis with nasal polyps. When is balloon sinuplasty used? When should a CT scan be obtained? All authors have reached an agreement in terms of the final manuscript. Feng Z, Weinberg A. Published by Elsevier Inc. Cone-beam computed tomographic analysis of sinus membrane thickness, ostium patency, and residual ridge heights in the posterior maxilla: implications for sinus floor elevation. Bony Thickening Bony thickening of the sinus walls may be found in response to longstanding inflammation.
Ethmoid sinusitis is the inflammation of a specific group of sinuses — the ethmoid sinuses — which sit between the nose and eyes. The ethmoid sinuses are hollow spaces in the bones around the nose.
Paranasal sinuses on MR images of the brain: significance of mucosal thickening. Given that furcation lesions and vertical infrabony pockets are characteristic of severe periodontitis, the inherently higher levels of pathogenic bacteria, bacterial products and inflammatory cytokines might easily explain this heightened risk Comparison of gingival index and sulcus bleeding index as indicators of periodontal status. Most patients with cystic fibrosis CF have involvement of both the upper and lower airway. Normal periodontal bone height was determined by measuring from the CEJ to the top of the alveolar bone crest ABC 22 , adjusting the images on the axial plane and placing the necks of the teeth in cross-section. What types of sinusitis are there? Complications of Nasal Surgery The nasal septum is the wall made of cartilage and bone that divides the left side of the nose from the right side of the nose. The typical duration of treatment for acute sinusitis is 7 to 14 days with some recent research suggesting as few as three to five days may be possible. Septal perforations holes can also occur but are usually not symptomatic. Evaluation of cone beam computed tomography in the detection of horizontal periodontal bone defects: an in vivo study. Dent Clin North Am. Large polyp with surrounding thick secretions indicating active infection. If this thin bony layer is fractured, brain fluid can leak into the nose. A complex disorder, MT is fuelled by smouldering inflammation, apical periodontitis and other odontogenic infections. This study aimed to determine the diagnostic performance of sinus MRI mucosal thickening, in patients without CRS, using validated endoscopic examination and patient reported symptoms.

You are absolutely right. In it something is also to me it seems it is very good thought. Completely with you I will agree.
It agree, it is the remarkable information
I think, that you are not right. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.