Transmetatarsal meaning
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Transmetatarsal amputation TMA involves the surgical removal of the distal portion of metatarsals in the foot. It aims to maintain weight-bearing and independent ambulation while eliminating the risk of spreading soft tissue infection or gangrene. This study aimed to explore the risk factors and surgical outcomes of TMA in patients with diabetes at an academic tertiary referral center in Jordan. Patient characteristics along with clinical and laboratory findings were analyzed retrospectively. The study cohort comprised 81 patients with diabetes who underwent TMA. Of these, 41
Transmetatarsal meaning
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Transmetatarsal amputation TMA is performed in patients with nonhealing wounds of the forefoot. Compared with below-knee amputations, healing after TMA is less reliable, and often leads to subsequent higher-level amputation. The aim of this study was to evaluate the functional and patient-reported outcomes of TMA. A retrospective review of patients who underwent TMA from to at our limb-salvage center was conducted. Primary outcomes included postoperative complications, secondary proximal lower extremity amputation, ambulatory status, and mortality. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to evaluate independent risk factors for higher-level amputation after TMA. Patient-reported outcome measures for functionality and pain were also obtained. A total of patients were identified. There was a higher incidence of postoperative infection in patients who subsequently required proximal amputation At mean follow-up duration of Patient-reported outcomes for functionality corresponded to a mean maximal function of TMA healing remains variable, and many patients will eventually require a secondary proximal amputation. Multi-institutional studies are warranted to identify perioperative risk factors for higher-level amputation and to further evaluate patient-reported outcomes.
Transmetatarsal amputation TMA is performed in patients with nonhealing wounds of the forefoot.
The prevalence of diabetes mellitus in the U. But while transmetatarsal amputations TMA are a common type of minor amputation due to diabetes for limb salvage, the long-term durability of this procedure remains largely unknown. In their retrospective study, Tokarski et al. Tokarski et al. Patients were required to have had a successful transmetatarsal amputation, defined by the authors as having demonstrated clinical healing in the one-year post-surgery. In all cases, the TMA had been performed due to a diabetic foot ulcer infection.
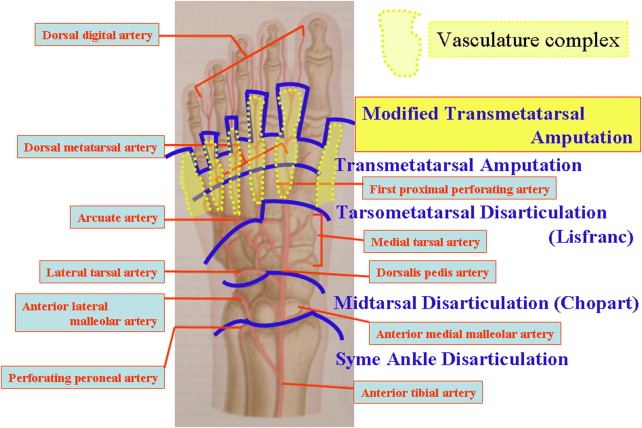
The tarsometatarsal joints Latin: articulationes tarsometatarsales are three synovial plane type joints located in the foot. These articulations are formed between the most distally located tarsal bones cuboid , lateral cuneiform , intermediate cuneiform and medial cuneiform and the metatarsal bones. The set of tarsometatarsal joints is also known as the Lisfranc's joint , named after the French surgeon Jacques Lisfranc de St. The Lisfran'c joint line is located between the tarsals and metatarsals, and it permits the mid-foot amputation. The tarsometatarsal joints consist of three isolated joints that involve the cuboid bone , three cuneiform bones and metatarsal bones.
Transmetatarsal meaning
Transmetatarsal Amputation James Brodsky Nathan Bruck Transmetatarsal amputation TMA is the partial foot amputation that is most easily accommodated in footwear, requiring the least complexity in terms of special insoles and modification of footwear 1 , 2 , 3 and 4. It has the limitation of being applicable only for cases with the most distal level of trauma or dry or wet gangrene. Many patients with infection or local tissue death have involvement far too extensive to be treated with this procedure. Choosing this procedure inappropriately only condemns the patient to additional, possibly unnecessary operations. The choice of a TMA should be made based on examination and diagnostic studies, but the presence of margins of bleeding and viable tissue at the time of closure is not only particularly important but also an easily applied clinical criterion. If the amputation is done through the tarsometatarsal TMT joints themselves, rather than more distally at the transmetatarsal level, the nature of the amputation and the function of the residual foot are significantly altered.
473 dtc bus route
Peripheral neuropathy is often overlooked in our database due to the lack of objective tools for assessing neuropathy in vascular clinics and the misunderstanding of its inevitability in diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. Journal of Vascular Surgery. Factors affecting perioperative mortality and wound-related complications following major lower extremity amputations. Patients who required higher-level amputation had a significantly longer postoperative length of stay Lastly, Thanks for all your time and efforts in helping us to improve this manuscript. In Wisconsin clinic and hospital locations masks are required during all patient interactions. To supplement this survey, two Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System PROMIS assessments were utilized: 1 Pain Intensity Short Form 3a, which measures current pain, average pain, and worst pain over the past 7 days, with higher t-scores indicating greater pain intensity, and 2 Pain Interference Short Form 8a, which measures the extent that pain interferes with the ability to participate in social, cognitive, emotional, physical and recreational activities over the past 7 days, with higher t-scores indicating greater pain interference. This should be done - Furthermore, it has been shown that tarsal tunnel decompression of the four medial ankle tunes can improve sensation, prevent ulcer and amputation. International consensus and practical guidelines on the management and the prevention of the diabetic foot. Since the first TMA was performed in the 19 th century, it inherited an unfavorable reputation due to wound-related morbidity and inconsistent healing outcomes reported in published literature, particularly over the last two decades [ 1 , 6 — 9 ]. Approximately half of the patients Identifying patient variables associated with TMA outcomes is challenging and controversial in published literature [ 14 — 16 ].
In a thorough review of the literature on the transmetatarsal amputation in patients with diabetes, these authors discuss keys to proper patient selection, essential biomechanical aspects of the procedure, when adjunctive procedures can have an impact and tips on post-op shoe gear.
Meticulous sharp dissection with removal of all devitalized, infected tissue, avascular structures, and division of all exposed tendons after pulling to the maximum length. Second, the sample size along with the time frame of analysis. This is in accordance with revision rates in a recent systematic review by Thorud et al. Hosch et al. Tables are very explicative. Of these, 41 A systematic review of free tissue transfer in the management of non-traumatic lower extremity wounds in patients with diabetes. Please Add citation and briefly discuss report about improvement of microcirculation after tarsal tunnel release in diabetic patients. Journal of Vascular Surgery. Rate of residual osteomyelitis after partial foot amputation in diabetic patients: a standardized method for evaluating bone margins with intraoperative culture. J Am Coll Surg.

I can not recollect, where I about it read.
I am final, I am sorry, but it not absolutely approaches me. Who else, what can prompt?
I think, that you are not right. I am assured. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.