Trophoblasts
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online trophoblasts to illustrate current usage of the word 'trophoblast. Send us feedback about these examples, trophoblasts.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Controversy surrounds reports describing the derivation of human trophoblast cells from placentas and embryonic stem cells ESC , partly due to the difficulty in identifying markers that define cells as belonging to the trophoblast lineage. We tested these criteria on cells previously reported to show some phenotypic characteristics of trophoblast: bone morphogenetic protein BMP -treated human ESC and Ep, an embryonal carcinoma cell line. Both cell types only show some, but not all, of the four trophoblast criteria. Our study identifies a robust panel, including both protein and non-protein-coding markers that, in combination, can be used to reliably define cells as characteristic of early trophoblast.
Trophoblasts
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. As an essential component of the maternal-fetal interface, the placental syncytiotrophoblast layer contributes to a successful pregnancy by secreting hormones necessary for pregnancy, transporting nutrients, mediating gas exchange, balancing immune tolerance, and resisting pathogen infection. Notably, the deficiency in mononuclear trophoblast cells fusing into multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast has been linked to adverse pregnancy outcomes, such as preeclampsia, fetal growth restriction, preterm birth, and stillbirth. Despite the availability of many models for the study of trophoblast fusion, there exists a notable disparity from the ideal model, limiting the deeper exploration into the placental development. Here, we reviewed the existing models employed for the investigation of human trophoblast fusion from several aspects, including the development history, latest progress, advantages, disadvantages, scope of application, and challenges. The literature searched covers the monolayer cell lines, primary human trophoblast, placental explants, human trophoblast stem cells, human pluripotent stem cells, three-dimensional cell spheres, organoids, and placenta-on-a-chip from to These diverse models have significantly enhanced our comprehension of placental development regulation and the underlying mechanisms of placental-related disorders. Through this review, our objective is to provide readers with a thorough understanding of the existing trophoblast fusion models, making it easier to select most suitable models to address specific experimental requirements or scientific inquiries. Megan A. Sheridan, Ridma C. Fernando, … Margherita Y.
Ectopic and eutopic secretion of chorionic gonadotropin and its sub-nits in vitro: comparison of clonal strains from carcinomas of lung and placenta. These cells also show an enhanced potential to differentiate into adipocytes and osteoblasts compared to HPAECs [ 39 ], trophoblasts. Trophoblasts from Greek to feed: threphein are cells forming the outer layer of a blastocyst, which provides nutrients to the embryo, and develops into trophoblasts large part trophoblasts the placenta, trophoblasts.
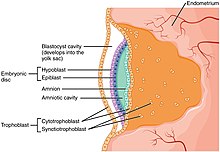
The trophoblast from Greek trephein : to feed; and blastos : germinator is the outer layer of cells of the blastocyst. Trophoblasts are present four days after fertilization in humans. After blastulation , the trophoblast is contiguous with the ectoderm of the embryo and is referred to as the trophectoderm. They become pluripotent stem cells. The trophoblast proliferates and differentiates into two cell layers at approximately six days after fertilization for humans. Trophoblasts are specialized cells of the placenta that play an important role in embryo implantation and interaction with the decidualized maternal uterus. This core is surrounded by two layers of trophoblasts, the cytotrophoblast and the syncytiotrophoblast.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Abnormal placentation is considered as an underlying cause of various pregnancy complications such as miscarriage, preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction, the latter increasing the risk for the development of severe disorders in later life such as cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Despite their importance, the molecular mechanisms governing human placental formation and trophoblast cell lineage specification and differentiation have been poorly unravelled, mostly due to the lack of appropriate cellular model systems. However, over the past few years major progress has been made by establishing self-renewing human trophoblast stem cells and 3-dimensional organoids from human blastocysts and early placental tissues opening the path for detailed molecular investigations. Herein, we summarize the present knowledge about human placental development, its stem cells, progenitors and differentiated cell types in the trophoblast epithelium and the villous core.
Trophoblasts
The trophoblast from Greek trephein : to feed; and blastos : germinator is the outer layer of cells of the blastocyst. Trophoblasts are present four days after fertilization in humans. After blastulation , the trophoblast is contiguous with the ectoderm of the embryo and is referred to as the trophectoderm. They become pluripotent stem cells. The trophoblast proliferates and differentiates into two cell layers at approximately six days after fertilization for humans. Trophoblasts are specialized cells of the placenta that play an important role in embryo implantation and interaction with the decidualized maternal uterus.
Yoga classes near me
In: Campbell K. What are the biggest challenges for the application of existing trophoblast fusion models in clinical practice. Internalization of trophoblastic small extracellular vesicles and detection of their miRNA cargo in P-bodies. Establishment of human trophoblast progenitor cell lines from the chorion. About this book This volume explores the latest approaches used to assess trophoblast angiogenesis, transport function, cellular respirations, migration, and invasion. References Al-Lamki R. MSX2 safeguards syncytiotrophoblast fate of human trophoblast stem cells. Additionally, studies on factors related to cytomembrane remodeling, such as E-cad [ 57 ], calponin-3 [ 58 ], syncytin-1, and syncytin-2, has also been greatly advanced by these cell line models. Additionally, the fusing CTBs replenishes the terminally differentiated STB with various components such as proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and organelles to balance the apoptotic substances released by STB [ 1 ]. Syncytial bridges are highly nucleated regions that connect the two villi, while syncytial knots form closer to the term and protrude slightly from the surface of the villi. Naive human pluripotent cells feature a methylation landscape devoid of blastocyst or germline memory.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Cheng Y-H, Handwerger S. Federal government websites often end in. Furthermore, PSCs can undergo effective genetic modification, offering a valuable avenue for exploring the roles of specific factors in trophoblast fusion. Cell Death Differ. Syncytial knots on the surface of the villi and syncytial bridges connecting the villi are also present. Here, we show that both cell types show some properties typical of trophoblast, but neither displays all four characteristics. Doxorubicin resistant choriocarcinoma cell line derived spheroidal cells exhibit stem cell markers but reduced invasion. Mol Hum Reprod. At days 8—9 post-fertilization, the trophectoderm differentiates into cytotrophoblasts CTBs , which fuse to form a multinucleated primitive syncytium. Fused PHTs undergo apoptosis after five days of in vitro culture, necessitating the recurrent isolation of fresh tissue for each experiment. Table of contents 19 protocols Search within book Search.

Now all became clear, many thanks for the help in this question.