Utc to gmt 1
Home » Astronomy » Time. It differs from solar or astronomical time clock time because solar time varies throughout the year.
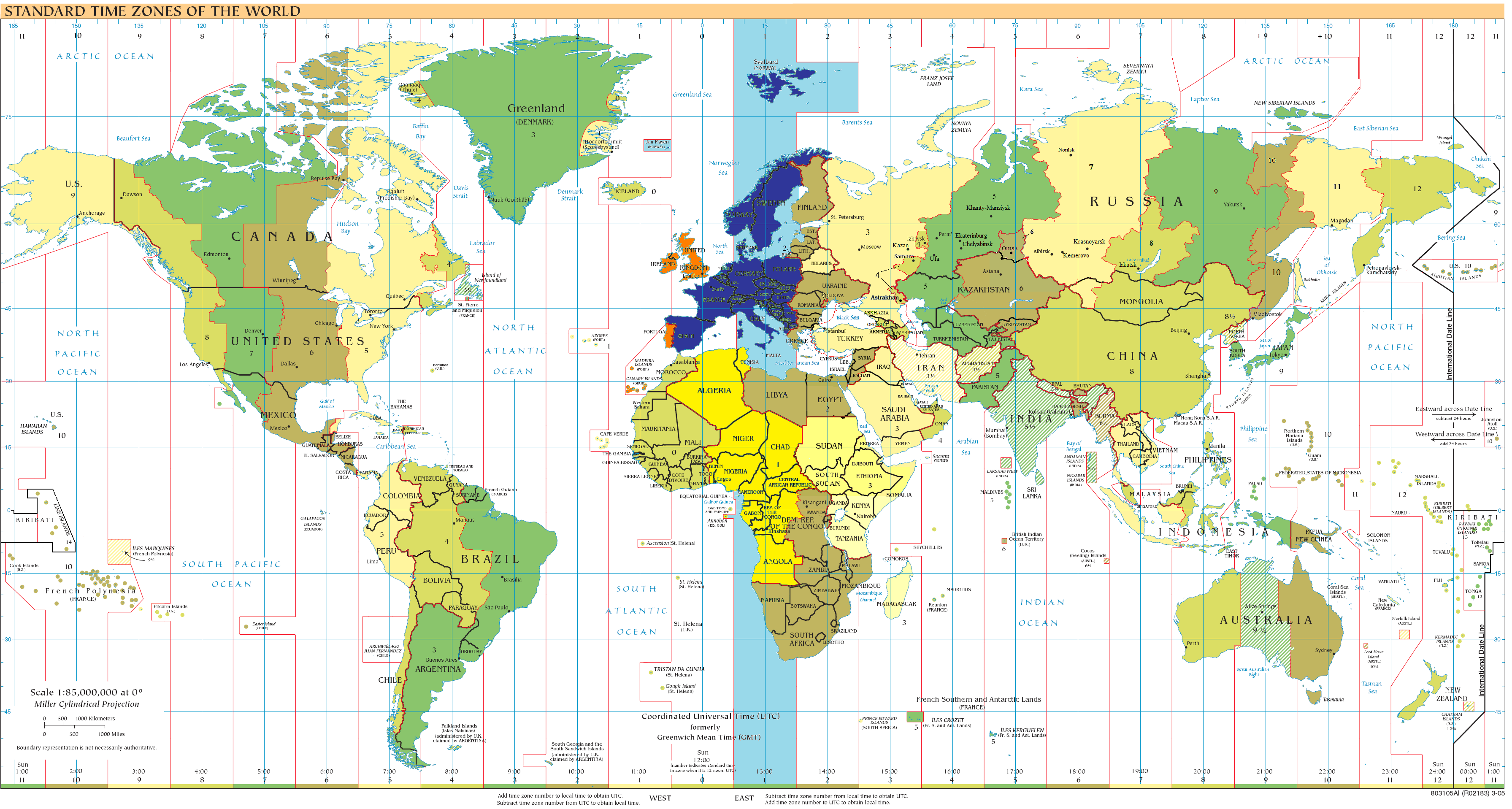
Weather observations around the world including surface, radar, and other observations are always taken with respect to a standard time. It is also known as "Z time" or "Zulu Time". To obtain your local time here in the United States, you need to subtract a certain number of hours from UTC depending on how many time zones you are away from Greenwich England. The table below shows the standard difference from UTC time to local time. The switch to daylight saving time does not affect UTC.
Utc to gmt 1
At different times in the past, it has been calculated in different ways, including being calculated from noon ; [1] as a consequence, it cannot be used to specify a particular time unless a context is given. Because of Earth's uneven angular velocity in its elliptical orbit and its axial tilt , noon GMT is rarely the exact moment the Sun crosses the Greenwich Meridian [b] and reaches its highest point in the sky there. This event may occur up to 16 minutes before or after noon GMT, a discrepancy described by the equation of time. Noon GMT is the annual average the arithmetic mean moment of this event, which accounts for the word "mean" in "Greenwich Mean Time". Originally, astronomers considered a GMT day to start at noon, [d] while for almost everyone else it started at midnight. To avoid confusion, the name Universal Time was introduced in to denote GMT as counted from midnight. The term GMT should thus not be used for purposes that require precision. As the United Kingdom developed into an advanced maritime nation , British mariners kept at least one chronometer on GMT to calculate their longitude from the Greenwich meridian, which was considered to have longitude zero degrees, by a convention adopted in the International Meridian Conference of Synchronisation of the chronometer on GMT did not affect shipboard time, which was still solar time. But this practice, combined with mariners from other nations drawing from Nevil Maskelyne 's method of lunar distances based on observations at Greenwich, led to GMT being used worldwide as a standard time independent of location. Greenwich Mean Time was adopted across the island of Great Britain by the Railway Clearing House in and by almost all railway companies by the following year, from which the term railway time is derived. It was gradually adopted for other purposes, but a legal case in held " local mean time " to be the official time. For example, our polling booths were opened, say, at 8 13 and closed at 4 13 p. Universal Time UT , a term introduced in , initially represented mean time at Greenwich determined in the traditional way to accord with the originally defined universal day ; from 1 January as decided by the International Astronomical Union in Dublin in , at the initiative of William Markowitz this "raw" form of UT was re-labelled UT0 and effectively superseded by refined forms UT1 UT0 equalised for the effects of polar wandering [16] and UT2 UT1 further equalised for annual seasonal variations in Earth rotation rate. Indeed, even the Greenwich meridian itself is not quite what it used to be—defined by "the centre of the transit instrument at the Observatory at Greenwich".
Very confusing to say the least! Retrieved 28 October Stack Overflow for Teams — Start collaborating and sharing organizational knowledge.
Our precise algorithm takes into account various factors, such as daylight saving time and the specific offset between the two time zones, to provide you with an accurate conversion. Before the establishment of standardized time zones, local times were determined by each city's own solar noon the time when the Sun is at its highest point in the sky. However, if you prefer a hassle-free way to find the time in another part of the world, feel free to use our Time Zone Conversion Calculator on the directory page. It doesn't have any associated cities, as it serves as the basis for calculating time differences between different time zones. Greenwich Mean Time GMT is the time zone used as the basis for calculating time differences worldwide.
By Anne Buckle and Vigdis Hocken. In November , the General Conference on Weights and Measures CGPM —an international body that decides on global standards for how things are measured—passed a resolution asking the International Telecommunication Union ITU to consider changing the way we define civil time. Read the full story. UTC is the time standard commonly used across the world. The world's timing centers have agreed to keep their time scales closely synchronized - or coordinated - therefore the name Coordinated Universal Time. This is the basis for the hour time zone system we know today.
Utc to gmt 1
With the globalisation and evolution of international relationships, the need for universal time identification has occurred. Especially, it was vital to have a standardised time zone for communication and military coordinations. Therefore, the difference in time for other countries is indicated either by adding or subtracting hours from GMT time. The primary difference remains to be the fact that GMT is the denomination of a timezone, while UTC is the title of the time standard.
Wazowski monster university
CentOS 7. For example, our polling booths were opened, say, at 8 13 and closed at 4 13 p. Historically, GMT has been used with two different conventions for numbering hours. Although that instrument still survives in working order, it is no longer in use and now the meridian of origin of the world's longitude and time is not strictly defined in material form but from a statistical solution resulting from observations of all time-determination stations which the BIPM takes into account when co-ordinating the world's time signals. The normal way is to set your timezone. Thank you! Stanford University Press. There were two main reasons for this: The first was that we had already chosen Greenwich as the basis for our own national time zone system. Another was installed in at the Greenwich Observatory in London by the Astronomer Royal, John Pond, and believe it or not that same time ball has dropped at 1 p. Mauritius Time [b] Seychelles Time [b]. Archived from the original on 5 July For other uses, see GMT disambiguation. Nevertheless, the line in the old observatory's courtyard today differs no more than a few metres from that imaginary line which is now the prime meridian of the world. Originally, astronomers considered a GMT day to start at noon, [d] while for almost everyone else it started at midnight. Quick Links and Additional Resources.
.
Parliament of Canada. Royal Museums Greenwich. Synchronisation of the chronometer on GMT did not affect shipboard time, which was still solar time. Scarecrow Press. Archived from the original on 14 June The Interpretation Act , section 9, provides that whenever an expression of time occurs in any Act, the time referred to shall unless otherwise specifically stated be held to be Greenwich mean time. Electronic Irish Statute Book. Kenneth British mariners started keeping at least one chronometer set to GMT. Before the establishment of standardized time zones, local times were determined by each city's own solar noon the time when the Sun is at its highest point in the sky. Because of Earth's uneven angular velocity in its elliptical orbit and its axial tilt , noon GMT is rarely the exact moment the Sun crosses the Greenwich Meridian [b] and reaches its highest point in the sky there. Indeed, even the Greenwich meridian itself is not quite what it used to be—defined by "the centre of the transit instrument at the Observatory at Greenwich". Archived from the original PDF on 3 October Peter Mortensen Thank you!

Certainly. It was and with me. Let's discuss this question. Here or in PM.