What is the specific heat of a substance
When summer hits, you might end up going to the beach to cool down. While the ocean waves may feel cool, the sand, unfortunately, is red-hot. If you aren't wearing shoes, it's possible to actually burn your feet!
In thermodynamics , the specific heat capacity symbol c of a substance is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the mass of the sample, also sometimes referred to as massic heat capacity or as the specific heat. Specific heat capacity often varies with temperature, and is different for each state of matter. The specific heat capacity of a substance, especially a gas, may be significantly higher when it is allowed to expand as it is heated specific heat capacity at constant pressure than when it is heated in a closed vessel that prevents expansion specific heat capacity at constant volume. Specific heat capacity is also related to other intensive measures of heat capacity with other denominators. One of the first scientists to use the concept was Joseph Black , an 18th-century medical doctor and professor of medicine at Glasgow University.
What is the specific heat of a substance
Heat capacity is an extensive property, so it scales with the size of the system. For example, if it takes 1, J to heat a block of iron, it would take 2, J to heat a second block of iron with twice the mass as the first. The heat capacity of most systems is not a constant. Rather, it depends on the state variables of the thermodynamic system under study. In particular, it is dependent on temperature itself, as well as on the pressure and the volume of the system, and the ways in which pressures and volumes have been allowed to change while the system has passed from one temperature to another. The temperature dependence is why the definition a calorie is formally the energy needed to heat 1 g of water from Different measurements of heat capacity can therefore be performed, most commonly at constant pressure and constant volume. The values thus measured are usually subscripted by p and V, respectively to indicate the definition. Gases and liquids are typically also measured at constant volume. Measurements under constant pressure produce larger values than those at constant volume because the constant pressure values also include heat energy that is used to do work to expand the substance against the constant pressure as its temperature increases. The internal energy of a closed system changes either by adding heat to the system or by the system performing work. Recalling the first law of thermodynamics,. If the heat is added at constant volume, then the second term of this relation vanishes and one readily obtains. This defines the heat capacity at constant volume , C V.
Two particular choices are widely used:. From the definition of entropy. Experiments show that the transferred heat depends on three factors: 1 The change in temperature, 2 the mass of the system, and 3 the substance and phase of the substance.
If a swimming pool and wading pool, both full of water at the same temperature, were subjected to the same input of heat energy, the wading pool would certainly rise in temperature more quickly than the swimming pool. The heat capacity of an object depends both on its mass and its chemical composition. Because of its much larger mass, the swimming pool of water has a larger heat capacity than the wading pool. Different substances respond to heat in different ways. If a metal chair sits in the bright sun on a hot day, it may become quite hot to the touch. An equal mass of water under the same sun exposure will not become nearly as hot.
If a swimming pool and wading pool, both full of water at the same temperature, were subjected to the same input of heat energy, the wading pool would certainly rise in temperature more quickly than the swimming pool. The heat capacity of an object depends both on its mass and its chemical composition. Because of its much larger mass, the swimming pool of water has a larger heat capacity than the wading pool. Different substances respond to heat in different ways. If a metal chair sits in the bright sun on a hot day, it may become quite hot to the touch. An equal mass of water under the same sun exposure will not become nearly as hot. Water is very resistant to changes in temperature, while metals generally are not. The table below lists the specific heats of some common substances. Notice that water has a very high specific heat compared to most other substances.
What is the specific heat of a substance
The learning objectives in this section will help your students master the following standards:. If two objects at different temperatures are brought in contact with each other, energy is transferred from the hotter object that is, the object with the greater temperature to the colder lower temperature object, until both objects are at the same temperature. There is no net heat transfer once the temperatures are equal because the amount of heat transferred from one object to the other is the same as the amount of heat returned. One of the major effects of heat transfer is temperature change: Heating increases the temperature while cooling decreases it. The symbol c stands for specific heat , and depends on the material and phase.
Millets hats
Constant-Pressure Calorimetry A constant-pressure calorimeter measures the change in enthalpy of a reaction occurring in solution during which the atmospheric pressure remains constant. September An Experimental Enquiry Concerning Potential energy stored in these internal degrees of freedom contributes to specific heat of the gas. How would you like to learn this content? However, attention should be made for the consistency of such ab-initio considerations when used along with an equation of state for the considered material. Heat capacity is an extensive property, so it scales with the size of the system. Measuring the heat capacity at constant volume can be prohibitively difficult for liquids and solids. Categories : Physical quantities Thermodynamic properties. The inner cup holds a known amount of a solute, usually water, that absorbs the heat from the reaction.
Heat capacity is an extensive property, so it scales with the size of the system. For example, if it takes 1, J to heat a block of iron, it would take 2, J to heat a second block of iron with twice the mass as the first. The heat capacity of most systems is not a constant.
That is, approximately,. September These parameters are usually specified when giving the specific heat capacity of a substance. Chemistry Physical Chemistry Specific Heat. How would you like to learn this content? Next, we will talk about the specific heat of water and why it is so important for life. The differences in heat capacities as defined by the above Mayer relation is only exact for an ideal gas and would be different for any real gas. The s pecific heat of water is relatively high at 4. However, it would be pretty inconvenient to measure the heat capacity of every unit of matter. This means that the amount of heat produced or consumed in the reaction equals the amount of heat absorbed or lost by the solution. Located at : www. It is

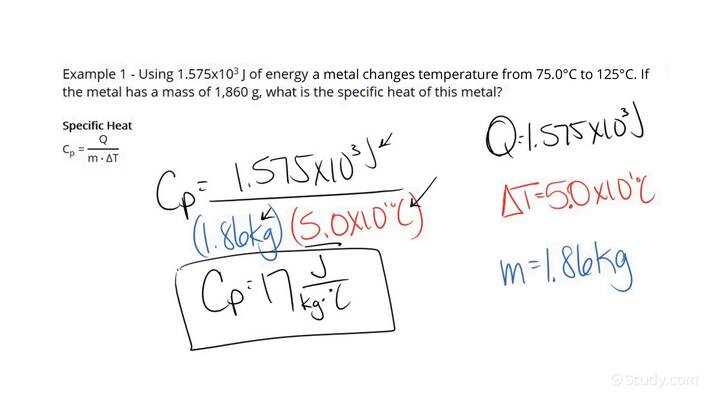
What is it to you to a head has come?
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you commit an error. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I like your idea. I suggest to take out for the general discussion.