Ato asset depreciation
The ATO depreciation rates determine tax deductions which represent the decline in value over time of assets which are associated with your income-earning activities. The media release dated 30 April is here.
Depreciating assets are assets used by a business that lose value over time through wear and tear, age and obsolescence. Examples include equipment, machinery, vehicles, furniture and computers. For tax purposes, businesses can claim a depreciation deduction to reflect the declining value of these assets as they are used for income producing purposes. Depreciation allows the cost of the asset to be distributed over its effective life, providing tax deductions over multiple years. For small businesses, depreciating assets and claiming depreciation deductions can significantly reduce their taxable income and tax liability. There are a few ways depreciation can be calculated:.
Ato asset depreciation
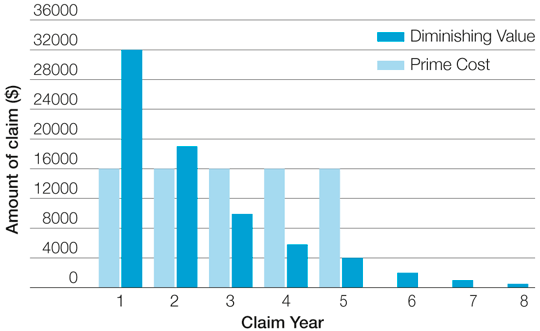
It often boils down to a lack of understanding about what depreciation is, how it works, and, most importantly, how to claim it. Knowing how to claim property tax depreciation can lead to substantial savings, making it a valuable strategy for optimising your investment returns. These items typically depreciate at a rate of 2. Division 40, on the other hand, refers to Plant and Equipment. This category includes removable or mechanical assets within the property, such as appliances e. The effective life of an asset is an estimate of the time in years that a depreciable asset can be used for income-producing purposes. The ATO provides guidelines on the effective life of various assets, which can be used to calculate their depreciation rates. The depreciation rate for plant and equipment assets is determined based on their effective life. The ATO uses two methods to calculate depreciation:. The prime cost method assumes that the value of a depreciating asset decreases uniformly over its effective life. On the other hand, the diminishing value method assumes that the value of a depreciating asset decreases more in the early years of its effective life. Therefore, the deductions are higher in the earlier years and decrease over time. The Commissioner of Taxation provides a guide that lists the effective life of many assets commonly found in rental properties. These estimates are designed to reflect the average time period over which a particular type of asset is likely to be used for income-producing purposes.
Self-managed super funds SMSFs have become an increasingly popular way for Australians to invest for retirement. Most intangible assets have an effective life which ato asset depreciation specified in the UCA depreciation rules, reproduced below.
The Ruling sets out the relevant principles identified by the Commissioner to assist in determining whether a composite asset is just one depreciating asset or a number of separate depreciating assets for tax depreciation Div 40 of the ITAA purposes. A composite asset is an asset that is comprised of multiple components that are capable of separate existence. The question arises as to how to deal with composite assets for the purposes of claiming a depreciation deduction. News Tax Fundamentals. New ATO ruling on depreciation of composite assets 19 Feb,
Disclaimer: While all the effort has been made to make this service as helpful as possible, this is free service and the author makes no warranties regarding the accuracy or completeness to any information on this website. Optical sound camera systems incorporating sound track and time code generators. Audio effects units incorporating aural exciters, compressors, delay and effects control processors graphic equalisers, harmonisers, limiters, noise reduction processors, reverberation processors, telephone simulators and time controllers. Digital sound conversion processors including encoders and decoders. Digital audio players, digital film projectors and digital sound conversion processors.
Ato asset depreciation
The ATO depreciation rates determine tax deductions which represent the decline in value over time of assets which are associated with your income-earning activities. The media release dated 30 April is here. More info here. Eligible costs will include business expenses and depreciating assets that support digital adoption, such as portable payment devices, cyber security systems or subscriptions to cloud-based services. Full Expensing Measures Extended to 30 June Announced as part of Budget measures, the availability of full expensing is extended by a further year until 30 June Budget Paper No. When assets decline in value, that represents an economic loss. ATO depreciation is all about recognising that loss as a tax deduction.
Great lakes brewery
The effective life method provides businesses with flexibility to determine the most appropriate depreciation rate for their specific assets based on expected usage. For information about the self-assessment process, see: Self Assessment of Depreciation rates. For further information see legislation and How it works. Stay informed with our newsletter Join our weekly newsletter and get our blogs and podcasts sent straight to your inbox. The ATO uses two methods to calculate depreciation:. However, this proposal was dropped in the Labor budget of 25 October There are general rules which apply under the uniform capital allowance system, provided by rules set out in the Income Tax Assessment Act These expenses would otherwise have been treated as black hole expenses and written off over 5 years. Note the termination of this concession from 1 January Eligible costs will include business expenses and depreciating assets that support digital adoption, such as portable payment devices, cyber security systems or subscriptions to cloud-based services. These estimates are designed to reflect the average time period over which a particular type of asset is likely to be used for income-producing purposes. Enabling legislation was passed by parliament on 13 August
Conceptually, depreciation is the reduction in the value of an asset over time due to elements such as wear and tear.
The ATO sets guidelines for the effective life and depreciation rates of different types of depreciating assets to assist businesses in calculating their depreciation deductions for tax purposes. The reason? For a calculator which converts effective life to a depreciation percentage rate — see: Converting Effective Life to the percentage depreciation rate — spreadsheet calculator. Full Expensing Measures Extended to 30 June Announced as part of Budget measures, the availability of full expensing is extended by a further year until 30 June Company Required. See more details here: Rental property tax deductions. The choice between these two methods depends on your strategy and cash flow needs. Self-managed super funds SMSFs have become an increasingly popular way for Australians to invest for retirement. To claim depreciation, businesses must keep records showing the cost of each asset, when it was purchased and its expected useful life. Change Location Find awesome listings near you! Self-assessment of effective life of patents etc. See also Traps with tax depreciation incentives. Budget Papers No. The Ruling sets out the relevant principles identified by the Commissioner to assist in determining whether a composite asset is just one depreciating asset or a number of separate depreciating assets for tax depreciation Div 40 of the ITAA purposes. Excluded is software which is trading stock or which is deductible elsewhere under the tax rules, or which is in the nature of an annual renewal or subscription which would be fully deductible as a business outgoing.

0 thoughts on “Ato asset depreciation”