Burst fracture radiology
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October
There is a comminuted burst 3 column fracture involving the L1 vertebra, including a large retropulsed fragment causing significant stenosis of the central canal. Bilateral L1 transverse process fractures. Minimally displaced fracture through the T12 spinous process is also noted. No hepatic or splenic laceration or hematoma identified. No intraperitoneal free gas or fluid. The adrenals, kidneys and pancreas are normal.
Burst fracture radiology
Fifty percent of TL fractures are unstable and can result in significant anatomic injury and deformity 4. Clinical assessment of patients with TL fractures is often challenging and, as a result, diagnostic imaging usually plays an essential role in their exact diagnosis and appropriate management 6. The aim of this article is to review the role of different imaging methods in studying TL fractures, emphasizing the role of the radiologist in classifying and quantifying the severity of these fractures. Radiographs are the adequate starting modality for patients who have sustained a low-energy trauma. AP and lateral views are usually performed. Both projections are useful in assessing vertebral height and the presence of fracture lines. The AP view allows the measurement of the interpedicular distance, which is increased in burst fractures, and the interspinous distance, which is increased in posterior ligamentous complex PLC injuries. These values can be reported as millimeters or as a percentage relative to adjacent normal levels. Regarding interspinous distance, variations of up to 7 mm are considered as normal 7. On lateral radiographs the two main parameters to be measured are vertebral height loss and kyphotic deformity 6 Figure 2. Kyphosis is the most common deformity observed in TL spine fractures and there are several ways to quantify it. Local vertebral kyphosis angle is measured between the tangent to the upper endplate and the lower endplate of the injured vertebra. We have to be reminded that vertebral wedging is not always synonymous of vertebral fracture. In normal children and adults, the vertebral body is anteriorly wedged from T1 through L2 peak at T7 , non-wedged at L3, and posteriorly wedged at L4 to L5 peak at L5 9. The superior limits of normal wedging have been reported in the literature as a ratio between the anterior and posterior vertebral height.
Eighty patients whom exposed spinal trauma and had burst fracture were evaluated concerning age, sex, fracture segment, neurological deficit, secondary organ injury and radiological changes that burst fracture radiology. You can see the edema related to the fracture of the vertebral body and the massive edema in the paraspinous muscles. Radiology Assistant Information.
Burst fractures are a type of compression fracture related to high-energy axial loading spinal trauma that results in disruption of a vertebral body endplate and the posterior vertebral body cortex. Retropulsion of posterior cortex fragments into the spinal canal is frequently included in the definition. However, some authors, including the popular AO spine classification system, define a burst fracture as any axial compression fracture involving an endplate and the posterior cortex regardless of retropulsion 6. They usually present as back pain and or lower limbs neurologic deficits in the clinical scenario of trauma. Two-level burst fractures are much less common than single-level burst fractures 2. Burst fractures involve the posterior wall of the vertebral body can be described as incomplete one endplate or complete both endplates 5.
Skip to content. Our team of dedicated access representatives is here to help you make an appointment with the specialists that you need. A burst fracture is an injury in which the vertebra, the primary bone of the spine, breaks in multiple directions. The bones of the spine have two main sections. The vertebral arch is a ring-shaped section that forms the roof of the spinal canal and protects the spinal cord. You can feel the spinous process , a projection from this arch, when you press on the skin in the middle of your back. The vertebral body is the cylindrical shaped portion of the vertebral bone that lies in front and provides the majority of structural support. In a burst fracture, the vertebral body shatters. A burst fracture usually results from significant trauma that compresses the bone, such as a motor vehicle accident or a severe fall. There are a number of different classification schemes to describe burst fracture and help direct their treatment.
Burst fracture radiology
A burst fracture is a type of spinal injury that occurs when an excessive force is applied to the spine, causing one or more vertebrae to break or shatter. This condition can lead to serious complications, including nerve damage, spinal cord injury, and chronic pain. This article will discuss the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for a burst fracture.
Ilife fiyat
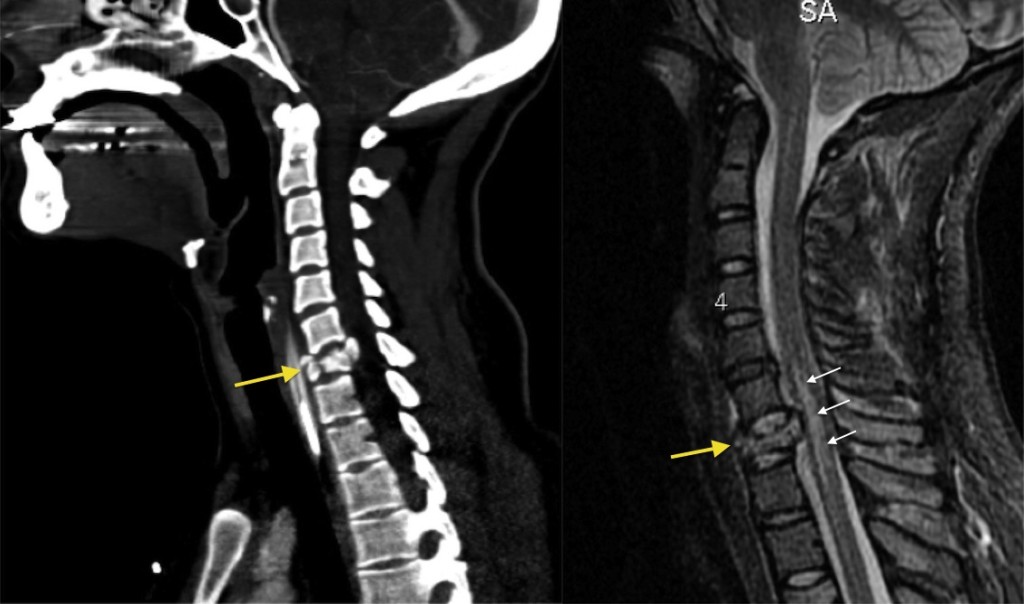
These fractures are usually fatal. A parameter can be scored points and the total score is the sum of these parameters with a maximum of 10 points. The interspinous ligaments are weak, thin, membranous structures connecting the adjacent spinous processes. Several radiological signs have been described to support this differential diagnosis, with MRI playing the main role in this task due to its capacity to detect fractures before radiographic morphologic changes appear The teaching point is: pay careful attention to little pieces of bone. Morphologic signs are a convex vertebral border, due to vertebral cortex expansion by a growing tumor, and the presence of an asymmetric paravertebral mass Figure 7 Patients with more than five points in this score system should undergo surgical intervention Arthritis Arthritis. Compression-distraction instrumentation of unstable thoracolumbar fractures: anatomic results obtained with each type of injury and method of instrumentation. Severe thoracolumbar injuries may present acutely with loss of motor and sensory function below the umbilicus T10 level. Presentation Fall 4. Case 4 Look at the images. A Sagittal reformatted image of the cervical spine.
Burst fractures are a type of compression fracture related to high-energy axial loading spinal trauma that results in disruption of a vertebral body endplate and the posterior vertebral body cortex. Retropulsion of posterior cortex fragments into the spinal canal is frequently included in the definition.
Int J Clin Exp Med. J Bone Joint Surg. These changes as an indicator of energy that is exposed can also give a hint for secondary organ injury and neurological deficit. The AP view allows the measurement of the interpedicular distance, which is increased in burst fractures, and the interspinous distance, which is increased in posterior ligamentous complex PLC injuries. Secondary organ injury was evaluated in the light of the abdominal CT reports and abdominal USG reports. Updating… Please wait. A new classification of thoracolumbar injuries: the importance of injury morphology, the integrity of the posterior ligamentous complex, and neurologic status. Pathologic fractures may show complete substitution of normal bone marrow or, when incomplete, tend to show and nodular or patchy pattern. Moreover, in our staging system, the proportion of dural injury was high in stage 2 and stage 3 patients. In case for which extension CT and non-extension radiographs are available, the degree of kyphotic correction as a sign of vertebral instability can be predicted They may occur as a result of cervical injuries from diving accidents or from rollover accidents in which the driver was not wearing a seat belt. Burst fracture This is the severe variant of a compression fracture with higher risk of neurologic deficits. American Spinal Injury Association. Both of these commonly used systems fail to systematically take into account the neurological status of the patient and the indication for MRI to determine the integrity of the posterior ligamentous complex. Only gold members can continue reading.

Quite