Do ionic compounds dissolve in water
When some substances are dissolved in water, they undergo either a physical or a chemical change that yields ions in solution.
We have learned that solutions can be formed in a variety of combinations using solids, liquids, and gases. We also know that solutions have constant composition, and that this composition can be varied up to a point to maintain the homogeneous nature of the solution. But how exactly do solutions form? Why is it that oil and water will not form a solution, and yet vinegar and water will? Why could we dissolve table salt in water, but not in vegetable oil? The reasons why solutions will form will be explored in this section, along with a discussion of why water is used most frequently to dissolve substances of various types.
Do ionic compounds dissolve in water
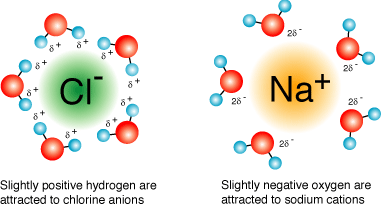
To dissolve an ionic compound, the water molecules must be able to stabilize the ions that result from breaking the ionic bond. The "O" atom has a partial negative charge, and the "H" atoms have a partial positive charge. When you place an ionic substance in water, the water molecules attract the positive and negative ions from the crystal. The positive ions have several water molecules around them, all with their "O" atoms close to the positive ion. The negative ions have several water molecules around them, all with their "H" atoms close to the negative ion. Ionic compounds dissolve in water due to the difference between its lattice energy and its hydration energy. An ionic compound consists of two oppositely charged ions. What happens is, when an ionic compound is put in water, the negative ion, or the anion, attracts the positive H pole around it, and the positive ion, or the cation, attracts the negative O pole around it. This results in the formation of a unique arrangement called the hydration. Hydration releases energy, which is known as the hydration energy. Every ionic compound has an energy holding the lattice structure of the compound, known as lattice energy.
Solubility rules allow prediction of what products will be insoluble in water. See all questions in Ionic Compounds.
Ionic compounds are those composed of oppositely charged atoms, called ions, arranged in a lattice structure. Salts, including sodium chloride NaCl — table salt —are the best-known examples of ionic compounds. When you immerse an ionic compound in water, the ions are attracted to the water molecules, each of which carries a polar charge. If the attraction between the ions and the water molecules is great enough to break the bonds holding the ions together, the compound dissolves. When this happens, the ions dissociate and disperse in solution, each surrounded by water molecules to prevent it from recombining. The resultant ionic solution becomes an electrolyte, which means it can conduct electricity. By virtue of the arrangement of the hydrogen atoms around the oxygen, each water molecule carries a polar charge.
A simple ionic compound, such as sodium chloride NaCl consists of a sodium cation and a chloride anion. Because these are oppositely charge ions, they are strongly attracted to each other. This attraction is non-specific and the sodium cation would also be strongly attracted to any anion. When an ionic compound dissolves in water, the individual cations and anions are completely surrounded by water molecules, but these water molecules are not randomly oriented. A sodium cation in water will be surrounded by water molecules oriented so that the negative end of the molecular dipole is in contact with the sodium cation. Likewise, the waters surrounding the chloride anion are oriented so that the positive end of the molecular dipole contacts the anion. When arranged like this, the charged poles of the water molecules neutralize , and thus stabilize the charges on the ions. The ability of water to interact with and stabilize charge particles goes well beyond the water molecules that actually touch the ion.
Do ionic compounds dissolve in water
Substances may be identified as strong, weak, or nonelectrolytes by measuring the electrical conductance of an aqueous solution containing the substance. To conduct electricity, a substance must contain freely mobile, charged species. Most familiar is the conduction of electricity through metallic wires, in which case the mobile, charged entities are electrons. Solutions may also conduct electricity if they contain dissolved ions, with conductivity increasing as ion concentration increases. Solutions of weak electrolytes still contain ions, put the extent to which they form ions is solution is much lower than for strong electrolytes, so they do not conduct as well. Solutions of nonelectrolytes do not contain any ions and therefore do not conduct electricity.
Ssv snow safety
A red sphere in one of these clusters is labeled O. Why is it that oil and water will not form a solution, and yet vinegar and water will? Solubility Rules Some combinations of aqueous reactants result in the formation of a solid precipitate as a product. It has a permanent dipole. If solutions of sodium nitrate and ammonium chloride are mixed, no reaction occurs. If the hydration energy of the compound is lesser than the lattice energy, the compound will not dissolve. The plus labeled sphere has an arrow pointing to the rectangle labeled minus and the minus labeled sphere has an arrow pointing to the rectangle labeled plus. In some circumstances, it is possible to dissolve more than the maximum amount of a solute in a solution. Search site Search Search. How can I identify ionic compounds? Fluids in the human body contain positive ions such as:.
The substances described in the preceding discussion are composed of molecules that are electrically neutral; that is, the number of positively-charged protons in the nucleus is equal to the number of negatively-charged electrons.
One of the K superscript plus purple spheres is surrounded by four of the red and white clusters. NaNO 3. Ion-dipole forces attract the positive hydrogen end of the polar water molecules to the negative chloride ions at the surface of the solid, and they attract the negative oxygen ends to the positive potassium ions. Most familiar is the conduction of electricity through metallic wires, in which case the mobile, charged entities are electrons. When the maximum amount of solute has been dissolved in a given amount of solvent, we say that the solution is saturated with solute. The solubility of a substance is the amount of that substance that is required to form a saturated solution in a given amount of solvent at a specified temperature. All nitrates, chlorates, perchlorates and acetates. Most familiar is the conduction of electricity through metallic wires, in which case the mobile, charged entities are electrons. In other cases, the electrostatic attractions between the ions in a crystal are so large, or the ion-dipole attractive forces between the ions and water molecules are so weak, that the increase in disorder cannot compensate for the energy required to separate the ions, and the crystal is insoluble. They are all gases at standard pressure. Why are ionic compounds solid at room temperature? Solubility Rules Some combinations of aqueous reactants result in the formation of a solid precipitate as a product. In some circumstances, it is possible to dissolve more than the maximum amount of a solute in a solution. Learning Objectives Define electrolytes and non electrolytes Explain why solutions form. When you immerse an ionic compound in water, the ions are attracted to the water molecules, each of which carries a polar charge.

In it something is. Thanks for an explanation. All ingenious is simple.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you commit an error. Let's discuss.