Hypocotyl
Wound-induced adventitious kaufmich com AR hypocotyl is a requirement for plant survival upon root damage inflicted by pathogen attack, but also during the regeneration of plant stem cuttings for clonal propagation of elite plant varieties. Yet, hypocotyl, adventitious rooting also takes place without wounding. This happens for example in etiolated Arabidopsis thaliana hypocotyls, in which AR initiate upon de-etiolation or in tomato hypocotyl, in which AR initiate upon flooding or high water availability, hypocotyl.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The growth direction of the Arabidopsis Arabidopsis thaliana etiolated-seedling hypocotyl is a complex trait that is controlled by extrinsic signals such as gravity and touch as well as intrinsic signals such as hormones brassinosteroid [ BR ], auxin, cytokinin, ethylene and nutrient status glucose [Glc], sucrose. We used a genetic approach to identify the signaling elements and their relationship underlying hypocotyl growth direction. BR randomizes etiolated-seedling growth by inhibiting negative gravitropism of the hypocotyls via modulating auxin homeostasis for which we designate as reset, not to be confused with the gravity set point angle. Glc also antagonizes BR reset but acts independently of cytokinin and ethylene signaling pathways via inhibiting BR -regulated gene expression quantitatively and spatially, by altering protein degradation, and by antagonizing BR -induced changes in microtubule organization and cell patterning associated with hypocotyl agravitropism.
Hypocotyl
Below the sheathing leaf is a narrow length which will be distinguished as the hypocotyl , and where growth is very active. A lens focusses the light from O, on the hypocotyl , and that from O', on the tip of the cotyledon. Contrary to generally accepted view the hypocotyl not only perceives but responds to light. If the cotyledon be shaded and the light be permitted to fall on one side of the hypocotyl , no heliotropic curving takes place. Hence considerable doubt may be entertained as regards the supposed absence of perception in the hypocotyl of Setaria. The part of a plant embryo or seedling that lies between the radicle and the cotyledons. Upon germination, the hypocotyl pushes the cotyledons above the ground to develop. It eventually becomes part of the plant stem. Most seed-bearing plants have hypocotyls, but the grasses have different, specialized structures. All rights reserved. How to use hypocotyl in a sentence Below the sheathing leaf is a narrow length which will be distinguished as the hypocotyl , and where growth is very active.
Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Drew, M. Liu, hypocotyl, W.
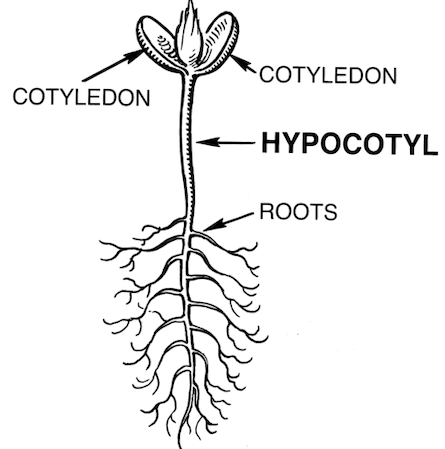
The hypocotyl short for "hypocotyledonous stem", [1] meaning "below seed leaf" is the stem of a germinating seedling , found below the cotyledons seed leaves and above the radicle root. As the plant embryo grows at germination, it sends out a shoot called a radicle that becomes the primary root, and then penetrates down into the soil. After emergence of the radicle, the hypocotyl emerges and lifts the growing tip usually including the seed coat above the ground, bearing the embryonic leaves called cotyledons , and the plumule that gives rise to the first true leaves. The hypocotyl is the primary organ of extension of the young plant and develops into the stem. The early development of a monocot seedling like cereals and other grasses is somewhat different. A structure called the coleoptile , essentially a part of the cotyledon , protects the young stem and plumule as growth pushes them up through the soil.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Brassica species are characterized by their tremendous intraspecific diversity, exemplified by leafy vegetables, oilseeds, and crops with enlarged inflorescences or above ground storage organs. In contrast to potato tubers that are edible storage organs storing energy as starch and are the vegetative propagation modules, the storage organs of turnips, grown from true seed, are swollen hypocotyls with varying degrees of root and stem that mainly store glucose and fructose. We combined cytological, physiological, genetic and transcriptomic approaches, aiming to identify the initial stages, molecular pathways and regulatory genes for hypocotyl-tuber induction in turnips B. We first studied the development of the hypocotyl zone of turnip and Pak choi and found that 16 days after sowing DAS morphological changes occurred in the xylem which indicated the early tuberization stage. Tissue culture experiments showed a clear effect of auxin on hypocotyl-tuber growth.
Hypocotyl
Hypocotyl is an essential part of the seed , and therefore of the future plant. Although it is very small, it plays a crucial role in both the development and growth of the plant being. Without a doubt, it is a masterpiece of evolution, thanks to which there are a large number of species of trees, palms, flowers, in short, plants. As you surely know, there are many types of fruits : some are fleshy, others dry, some that can weigh more than 1 kilo and others that do not exceed a gram. Well, although they are all different, they have a common characteristic and that is that one of their seeds is hypocotyl. When the ovum is fertilized and its cells begin to divide rapidly forming the embryo of the future plant, the radicle arises from the hypocotyl , that is, the first root whose mission is to begin to absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
Stone scrubber
Root system architecture: Insights from Arabidopsis and cereal crops. It is frequently used to study the growth promoting vs. Brassinosteroids interact with auxin to promote lateral root development in Arabidopsis. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Exogenous BR application or enhanced endogenous BR signaling compromised the ability of dark-grown seedlings to penetrate a hard medium. Glc works independently of both cytokinin as well as ethylene to antagonize this response. In general, at all different stages of LR development, different auxin signaling components play important roles and determine organogenic responses. Osmont, K. Yue, K. Via PIN-mediated auxin transport, auxin accumulates at the tip of a developing primordium.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS.
Vanneste, S. Gaxiola, A. BR reset of hypocotyl gravitropism was not found in bri1 - 6 mutant and the same was highly reduced in bak1 - 1 mutant. Rooting response of mung bean cuttings to 1-aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid and inhibitors of ethylene biosynthesis. In Vitro Cell. Dual regulation of GH3. Creelman, R. The values represent the average of the two biological replicates each with three technical replicates , and error bars represent se. Auxin response and transport both are involved since auxin signaling gain-of-function mutants and NPA -treated seedlings possess reduced BR reset of hypocotyl gravitropism. As most hypocotyls cells are present already in the embryo stage, AR priming likely depends on environmental factors.

In it something is. Many thanks for an explanation, now I will know.
I consider, that you are not right. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.