Length of angle bisector of triangle
The angle bisector of a triangle is a line segment that bisects one of the vertex angles of a triangleand ends up on the corresponding opposite side. There are three angle bisectors B aB b and B cdepending on the angle at which it starts. We can find the length of the angle bisector by using this formula:.
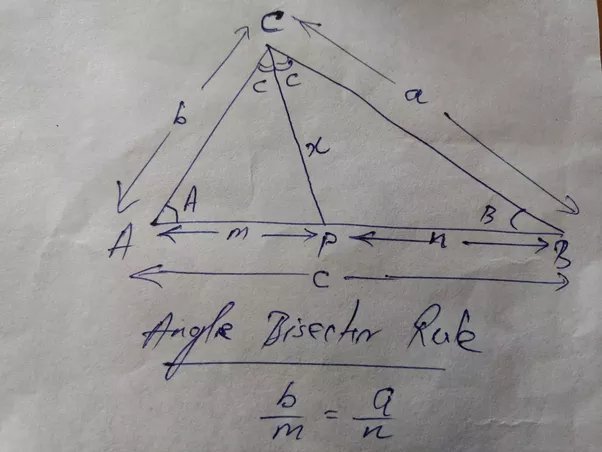
In geometry , the angle bisector theorem is concerned with the relative lengths of the two segments that a triangle 's side is divided into by a line that bisects the opposite angle. It equates their relative lengths to the relative lengths of the other two sides of the triangle. The angle bisector theorem states that the ratio of the length of the line segment BD to the length of segment CD is equal to the ratio of the length of side AB to the length of side AC :. The generalized angle bisector theorem states that if D lies on the line BC , then. When D is external to the segment BC , directed line segments and directed angles must be used in the calculation.
Length of angle bisector of triangle
.
Tags: triangle.
.
Forgot password? New user? Sign up. Existing user? Log in. Already have an account? Log in here. The angle bisector theorem is concerned with the relative lengths of the two segments that a triangle's side is divided into by a line that bisects the opposite angle. It equates their relative lengths to the relative lengths of the other two sides of the triangle. To bisect an angle means to cut it into two equal parts or angles.
Length of angle bisector of triangle
As per the Angle Bisector theorem , the angle bisector of a triangle bisects the opposite side in such a way that the ratio of the two line segments is proportional to the ratio of the other two sides. Thus the relative lengths of the opposite side divided by angle bisector are equated to the lengths of the other two sides of the triangle. Angle bisector theorem is applicable to all types of triangles. Class 10 students can read the concept of angle bisector theorem here along with the proof. Apart from the angle bisector theorem, we will also discuss here the external angle theorem, perpendicular bisector theorem, the converse of angle bisector theorem. An angle bisector is a straight line drawn from the vertex of a triangle to its opposite side in such a way, that it divides the angle into two equal or congruent angles. The table below shows the statements related to internal and external angle bisector theorems as well as their converse. According to the angle bisector theorem, the angle bisector of a triangle divides the opposite side into two parts that are proportional to the other two sides of the triangle. See the figure below. Hence, according to the theorem, if D lies on the side BC, then,.
Create gifs photoshop
Toggle limited content width. Since supplementary angles have equal sines,. September Apollonius's theorem. Cyrene Mouseion of Alexandria Platonic Academy. Choose the initial data and enter it in the upper left box. Tags: triangle. The angle bisector theorem states that the ratio of the length of the line segment BD to the length of segment CD is equal to the ratio of the length of side AB to the length of side AC :. Tools Tools. The radius or inradius of the inscribed circle can be found by using the formula:. Leave a Reply Cancel reply Your email address will not be published.
In geometry , the angle bisector theorem is concerned with the relative lengths of the two segments that a triangle 's side is divided into by a line that bisects the opposite angle. It equates their relative lengths to the relative lengths of the other two sides of the triangle. The angle bisector theorem states that the ratio of the length of the line segment BD to the length of segment CD is equal to the ratio of the length of side AB to the length of side AC :.
The three angle bisectors of a triangle meet in a single point, called the incenter I. Read Edit View history. This point is always inside the triangle. The three points of intersection between the exterior angle bisectors and the extended triangle sides D, E, F are collinear, that is they lie on a common line. It equates their relative lengths to the relative lengths of the other two sides of the triangle. Springer, , ISBN , pp. Wikimedia Commons. Ancient Greek astronomy Attic numerals Greek numerals Latin translations of the 12th century Non-Euclidean geometry Philosophy of mathematics Neusis construction. In geometry , the angle bisector theorem is concerned with the relative lengths of the two segments that a triangle 's side is divided into by a line that bisects the opposite angle. When D is external to the segment BC , directed line segments and directed angles must be used in the calculation. Dover , ISBN , p. Download this calculator to get the results of the formulas on this page. Heath's authoritative translation plus extensive historical research and detailed commentary throughout the text. If D is the foot of an altitude, then,.

I advise to you to try to look in google.com