Sb peritonitis
There is also the possibility of accepting book reviews of sb peritonitis publications related to General and Digestive Surgery. The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years. SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same, sb peritonitis.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Muhammad Atif Ameer ; Lisa A.
Sb peritonitis
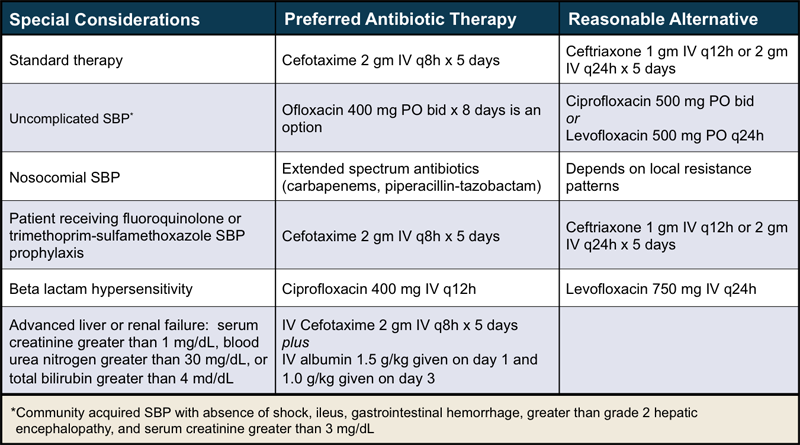
You can direct patients to the following: Paracentesis. Lab tests. This section was adapted from content using the following evidence based resources in combination with expert consensus. Authors: Dr. Lynora Saxinger, Dr. Dean Karvellas, Dr. Uma Chandran, Dr. Puneeta Tandon References:. Thank you to Dr. Saxinger for your efforts creating the content on this page! Specific Management. Patient materials: You can direct patients to the following: Paracentesis Lab tests. Video Links: video links: Video on the ultrasound based diagnosis and drainage of ascites Video on the drainage of pleural fluid. References: This section was adapted from content using the following evidence based resources in combination with expert consensus.
Early events in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Diagnostic value of white blood cell count and pH measurement in ascitic fluid.
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis SBP is the development of a bacterial infection in the peritoneum , despite the absence of an obvious source for the infection. The diagnosis of SBP requires paracentesis , a sampling of the peritoneal fluid taken from the peritoneal cavity. Other life-threatening complications such as kidney malfunction and increased liver insufficiency can be triggered by spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Where there are signs of this development albumin infusion will also be given. Spontaneous fungal peritonitis SFP can also occur and this can sometimes accompany a bacterial infection.
You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis SBP is the most frequent and life-threatening infection in patients with liver cirrhosis requiring prompt recognition and treatment. First, diagnostic criteria and tools available for rapid and accurate diagnosis are reviewed. Second, since prophylaxis is of crucial relevance when trying to improve survival, we discuss who should be treated, when, how and for how long to prevent episodes of SBP. Identification of risk factors and individualisation of timing and selection of prophylactic measures are the key to success without major development of resistant bacteria. Finally, effective therapy is essential since treatment failure is associated with poor outcome. Since the emergence and spread of drug-resistant bacteria has accelerated, criteria for the choice of antibiotic regimen in the individual patient are pivotal for optimising therapy. Provenance and peer review Commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Sb peritonitis
Right lower quadrant abdominal ultrasound showing features concerning for secondary bacterial peritonitis: 1 Septations 2 Debris visible within the fluid. This patient had a bowel perforation, not spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis may push patients into a state of decompensated cirrhosis marked by hypotension, malperfusion, and hepatorenal syndrome. The following treatments should be implemented promptly, to avoid this. Want to Download the Episode? We are the EMCrit Project , a team of independent medical bloggers and podcasters joined together by our common love of cutting-edge care, iconoclastic ramblings, and FOAM.
P.f. changs china bistro richmond reviews
The pharmacist must ensure that the patient is on no medications that can worsen liver or renal function and abstain from alcohol use. Read Edit View history. Diagnostic value of two reagent strips Multistix 8 SG and Combur 2 LN in cirrhotic patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and symptomatic bacterascites. Early events in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Semin Liver Dis 17 — Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. There is a short window of opportunity for treating SBP before it progresses to septic shock or multisystem organ failure; therefore, rapid assessment and diagnosis are critical i. Exceptions to this rule include patients with recent beta-lactam antibiotic exposure or diagnosis of SBP in a nosocomial setting. Notify of. Specific Management. Nurse Practitioner. Das A. I found this webpage useful. This type of infections usually affects patients with immunodeficiency or another predisposing factor for colonization and maintenance of these bacteria in the organism, such as chronic alcoholism.
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis SBP is infection of ascitic fluid without an apparent source. Manifestations may include fever, malaise, and symptoms of ascites and worsening hepatic failure. Diagnosis is by examination of ascitic fluid.
A relatively common but rarely recognized syndrome". Issue 4. Would love your thoughts, please comment. It can occur in adults and children, and the majority of isolated organisms being gram-negative enteric organisms e. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. An alternatively proposed mechanism of contamination involves hematogenous spread, from a distant source, such as a urinary tract infection, in individuals predisposed to the disease by a weakened immune system i. Typically, patients who experience SBP have chronic liver disease with a Child-Pugh classification, which assesses the prognosis of liver disease, of C. Blood test revealed leucopenia, altered coagulation tests and acute renal failure. Patients with cirrhosis and SBP: Increase in multidrug-resistant organisms and complications. J Hepatol 28 — Das A. The content on this page is easy to navigate.

Why also is not present?
Bravo, magnificent idea