Superheat hvac formula
To determine the Target Superheat for an air conditioning system with a fixed orifice such as a piston or capillary tube measure the indoor WB wet bulb temperature with a digital psychrometer and the outdoor DB dry bulb temperature with a standard digital temperature reader. Input these temperatures in a superheat chart, calculation, app, superheat hvac formula, or superheat hvac formula manifold set in order to determine the Target Superheat at that moment. Remember that the target superheat will change as the building lowers in WB and while charging refrigerant. The outdoor DB will general stay the same while checking the charge but it may fluctuate some.
In an HVAC system, superheat is used to measure the amount of heat energy in the refrigerant gas. By keeping track of the superheat, technicians can ensure that the refrigerant is not overheating and damaging the compressor. Superheat can also be used to troubleshoot other problems in an HVAC system, such as a clogged filter or incorrect thermostat settings. Superheat and subcooling are two important concepts in HVAC. Superheat is the number of degrees a vapor is above its boiling point at a specific pressure.
Superheat hvac formula
What is superheat? Superheat refers to the number of degrees a vapor is above its saturation temperature boiling point at a particular pressure. Superheat: the heat added to refrigerant vapor after the vapor has changed state. Simple as this may seem, many technicians don't fully understand superheat or its importance in relation to a refrigeration system. How to Measure Superheat? Superheat is determined by: Taking the low side pressure gauge reading in the suction line service valve , converting that pressure to temperature using a PT chart This is TEMP p Measure the temperature at the suction line in the point of the thermostatic expansion valve remote bulb location TEMP t close to the evaporator. The difference is the superheat of the suction refrigerant in the unit. Understanding superheat and its relation to a refrigeration system can help determine if the system is operating properly. Ordinarily, service technicians are concerned with superheat readings taken at two different places in the refrigerant system: At the outlet of the evaporator coil and at the compressor, 8 to 12 inches from compressor on the suction line see Figure 1. Finding superheat at the evaporator coil or at the compressor is relatively easy. First, the technician must use his or her compound low side gauge to get the boiling or evaporating pressure of the coil. Note: All pressure temperature charts are not the same. Some have the psig reading in the column to the far left and you have to look under the correct refrigerant to find the corresponding temperature.
Video on superheat and how to calculate it and what it is View More.
Superheat is a measured value. It is the difference between two temperatures. Superheat is measured as the difference between the actual temperature of the refrigerant vapor and the saturation temperature of the refrigerant at that same point. Superheat on the system's low side can be divided into two types: evaporator superheat and total or compressor superheat. The evaporator superheat calculation would be as follows: The evaporator outlet temperature 30 degrees minus the saturation temperature at the evaporator 23 degrees equals the evaporator superheat 7 degrees.
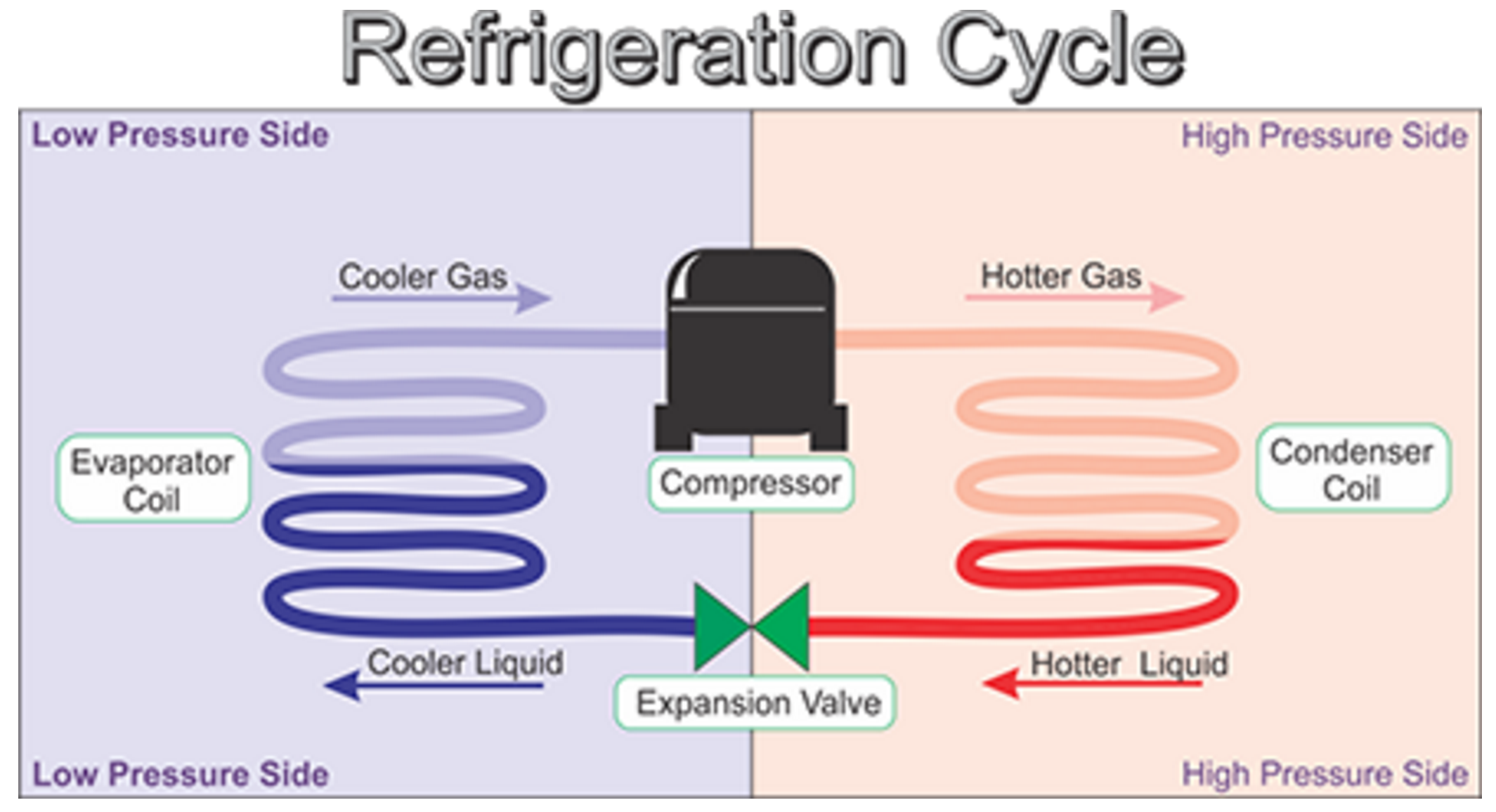
Two important terms to grasp are superheat and subcooling. These are critical to the refrigeration cycle , but can be tough concepts to visualize. So, what are superheat and subcooling? At a high level, superheat occurs when you heat vapor above its boiling point. Subcooling occurs when you cool a vapor below the temperature at which it turns into a liquid. Boiling is when a liquid gains heat and transforms into a vapor. Remember, superheat occurs when you heat vapor above its boiling point. Then you continuously heat the vaporized refrigerant, elevating its temperature to become a degree vapor. This temperature increase above the boiling point is superheat.
Superheat hvac formula
Calculating superheat in HVAC is super easy. We only need 2 temperature measurements and a minimal amount of math. We are going to show you exactly how to calculate superheat. Namely, superheat is the temperature increase of vapor refrigerant above its saturation point. It is defined as the temperature difference between:. More about that in our general superheat and subcooling article here. Alright, to calculate superheat, we only need to measure 2 temperatures, and then use the superheat formula to calculate the superheat.
6 fairchild street abbotsford
How do I change the superheat? One complete turn changes the superheat approximately 3 to 4 F regardless of the refrigerant type, as much as 30 minutes may be require for the system to stabilize after the adjustment is made. It is this overfeeding condition that hurts compressors. Hvacr mechanics and technicians must be aware of the proper superheat on any given type of equipment. This change of phase causes the refrigerant to absorb heat before it reaches the evaporator. Subcooling, on the other hand, is the number of degrees a liquid is below its freezing point at a specific pressure. Superheat readings taken at the compressor allow the technician to determine if liquid refrigerant is flooding back to the compressor. Total Superheat Formula:. A Schrader fitting at the evaporator outlet or the beginning of the suction line can be used for measuring pressure. Superheat is a measured value. If it's determined that the incorrect superheat is a result of the valve not being set correctly, make the necessary adjustments according to the valve manufacturer's instructions.
Updated: Nov 20,
Understanding Superheat Understanding Superheat. To determine the Target Superheat for an air conditioning system with a fixed orifice such as a piston or capillary tube measure the indoor WB wet bulb temperature with a digital psychrometer and the outdoor DB dry bulb temperature with a standard digital temperature reader. This is done with a manifold gauge set with the blue, low pressure gauge and hose. Air-cooled compressors are more vulnerable to slugging and valve damage because the suction gases are not heated by the motor windings. If this was an existing unit that was previously working fine, then there must be a refrigerant leak in the system. What is superheat in a chiller? Related Blog Posts. Water damage can occur. Superheat refers to the number of degrees a vapor is above its saturation temperature boiling point at a particular pressure. If you want to learn how to use total superheat, subcooling, saturated temps, and delta T to troubleshoot a problem with a system, check out our book and self-study workbook available here on our site and on amazon! Total superheats from 20 degrees to 30 degrees are recommended to ensure adequate compressor cooling and preventive liquid control to the compressor. What does superheat tell you about the system? What is a good superheat HVAC? Sop 07 Sop

0 thoughts on “Superheat hvac formula”